
During the early 1970s. The international community adopted the terms Bio- Mechanics to describe the application of mechanical principles in the study of living organisms. As it was realized after 1950 that the mechanical principles involving on the human body is entirely different from other things.
Internal forces and take place under the effect of external forces eg. When we walk.
A background of mechanics can help coaches to know their sport more, make them more confident about their practice and extent their knowledge beyond the technique to know the scientific reason. They will be better prepared to answer-
Why we do it this way? Why should not I do this way? – Student deserves better answer than because as a coach- I said.
When the study of mechanics is limited to living structure, especially the human body, it is called Bio-mechanics.
The Bio-mechanics has derived from two words-Biomechanics.
Bio means, some thing pertaining to living being or life.
Mechanics -means, the discipline which studies the movement of object/motion of objects with the help of mechanical principles.
Mechanics is a branch of physics which study the object/ from mechanical point of view. So, the knowledge of Bio-mechanics used to study and analysis the movement of living things. Any object is moving, it depends upon the resultant of various forces acting on the body.
"The area of study where the knowledge and methods of mechanics are applied to the structure and function of the living human system"
"Bio-mechanics is the science concerned with the internal and external forces acting on a human body and the effects produced by these forces".
"It is a field of study based upon the anatomical and mechanical analysis of human motion".
- HAY & REID
"It is that branch of physics concern with the effect that forces have on bodies and the motion produced by these forces".
- WELL
"Science concerned with the internal and external forces acting on a human body and the effects produced by these forces".
- JAMES G. HAY
"Mechanical bases of biological especially to the Muscular activity and the principles and the relations involved there in".
-WEBSTER’S INT.DICTIONARY
The application of Mechanical laws of living structures, specially to the loco motor system of human body”.
"The area of study where the knowledge and methods of mechanics are applied to the structure and function of the living human system"
"Bio-mechanics is the science concerned with the internal and external forces acting on a human body and the effects produced by these forces.
KINESIOLOGY is the scientific study of human motion. The words kinesiology is taken by the combination of two Greek words-
| KINESIS | - | Movements or Motion |
| LOGIO | - | To speak-kinesiology means the science which speaks of movement or motion. |
| Movement | - | "Change in location or position the body." |
| Analysis | - | "It splitting up an object matter movement into its constituent parts or elements is called analysis". |
| Example | - | Long Jump (Constituent parts are) (i) Approach Run (ii) Take Off (iii) Movement in Air (iv) Landing |
KINESIOLOGICAL ANALYSIS
“Kinesiological analysis seeks to identify the joints, muscles and the body levers involved in execution of a given skills (movements) as well as the sequence and degree of their involvement”.
It involves the following steps.
1) Descriptive purpose - To cover a greater horizontal distance in a single leap by
take off by two leg.
Classify Motor Skill
2) Anatomical Analysis
i) Muscles-
i) Involvement of muscles in movements.
iii) Types of contraction
iv) Effect of contraction (full, medium or less)
3) Mechanical Analysis - Identification of mechanical principles for execution of S.B.J.
Body become projectile
Why Kinesiological Analysis ?
MECHANICS is that branch of science which studies the motion or form of bodies under the action of forces.
BIOMECHANICS - is the field of study which applies the principles of mechanics to the structure and movement of living things.
SPORTS BIOMECHANICS - is the application of the principles of biomechanics to the study of human motion in sports and exercise.
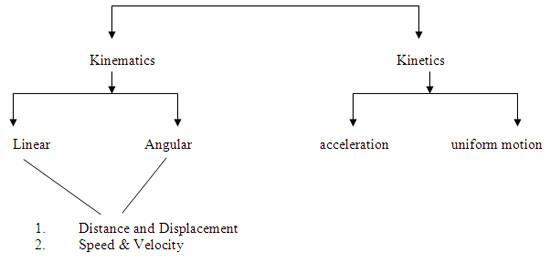
Bio-Mechanics - has two branches
Kinematics - Descriptive nature of movement
Kinetic - Cause of Motion
"It is the process of identification the Kinematics characteristics as well as kinetic basis of the movement structures".
Example - 100 mts.
Kinematics - It is characteristic of movement pattern.
i) Change in velocity
ii) Maintenance
iii) Declaration
One moves due to force from ground.
Kinetic i) How much force get from ground in running direction.
Two types of Analysis
i) Qualitative
ii) Quantitative
i) Qualitative - Concern with only identification of observable characteristics or performance is evaluated subjectively.
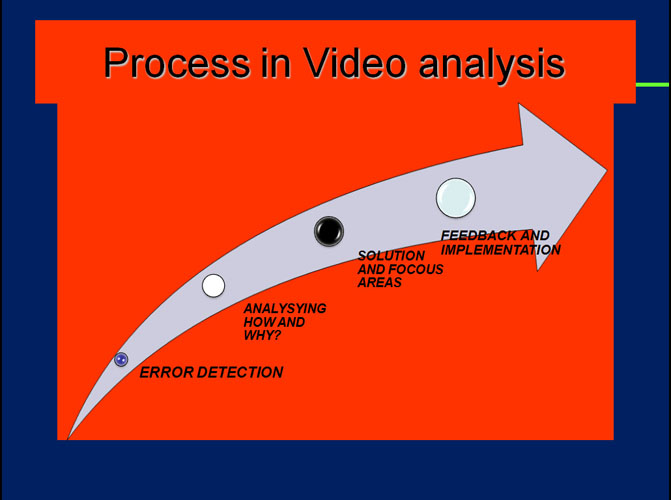
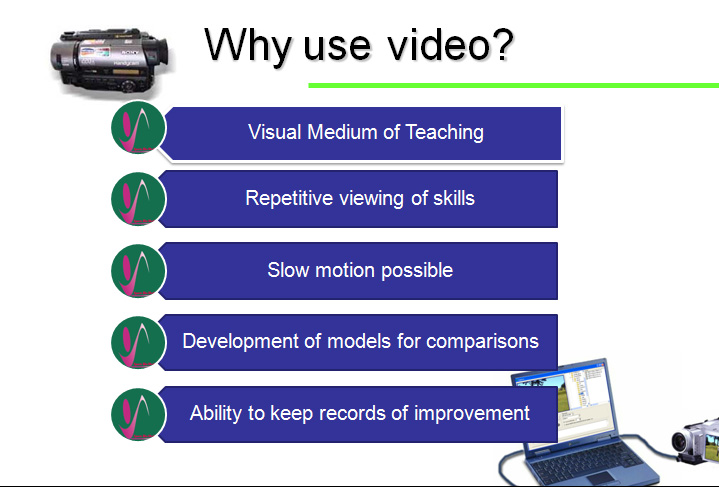
a) It is based on the visual observation of result or performance. Some time observation may be aided by instrument like Video-recording, because some time eyes are not able to catch total movement. Then Video recording enhance the analysis.
In its more complete form, the method consists of a systematic evaluation of not only the results but also of all the various factors that have contributed to result".
Example "Drive your chest forward and upward as you take off".
The advice is probably based on the coach's knowledge.
Uses of video-recording Polaroid sequence camera or a motion picture camera. – (result is not altered by the use of such aids)
ii) Quantitative Analysis - is based on measurements taken from a recorded the performance. It is basically objective.
"It is identify the factors that determine success in the performance of a motor stalls.
In Quantitative analysis - The performance is first recorded using photographs, cinematography, electromyography or some other recording technique, than is evaluated objectively on the basis of measurements taken from the record(s).
Example- study of sprinting
High speed motion picture film and analyze these frame by frame to determine such quantities as the horizontal and vertical velocity of the C.G. at critical instants through the sequence of motion. – at the instant of touch down and take off for each ground support phase.
We obtain some values or data and that data further treated for scientific interpretation for generalization and for statistical analysis"
Required
1- Expensive equipment
2- Highly trained people
3- More time
With Quantitative analysis, researcher would reach conclusions concerning the factors that determine success.
Bio-Mechanics in Physical Education, Sports & Research

Bio-mechanics is applied at all level of training and at all age.
Fundamental Skill
In the form of daily life activity or sport activity there are two types.
Each game composed of various skill and combination of these skill give rise to tactics.
Basic movement ensure efficiency of General movement pattern. If a person have mastery over the skill is more of that person.
Rough - coordination
Fine - coordination
Automatisation execution
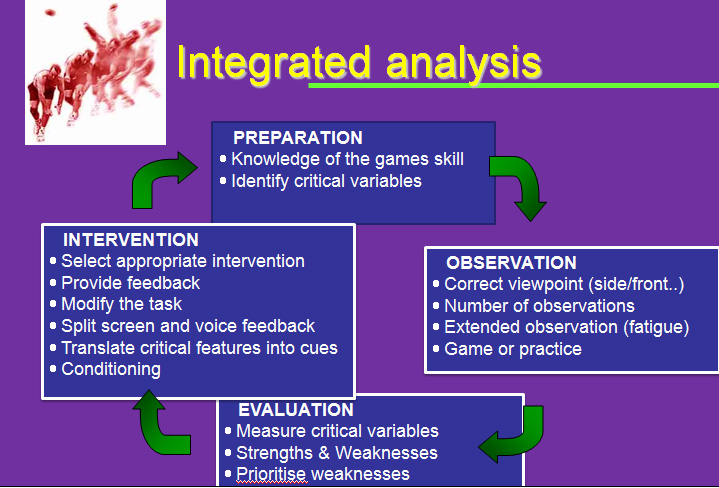
Mechanical Analysis – “is the process of identify all the laws and principles of mechanics. “A branch of physics which deals with motion and force which comes into play during the execution of a given motor skills of movement of a sports skill”.
Example – Spiking –Complex technique- require co-ordination ability – split up in its constituent phases –
1) Approach 2) Take off 3) Movement in the air
4)Hitting the ball 5) Landing
1) Approach – There stride approach and last stride longer the previous one with both the feet together to get Heel-ball-toe action-result to get leaner momentum (MXU) and last step change the linear momentum into angular momentum.
2) Take off – is result of ground reaction(New or III law) - Force + momentum
Force + Arm action
Take of Force
Take of angle
3) Movement in the air – Person arches back to acquire dynamic stability when the body is without supports (Law of end & middle law) when end move forward middle move backward use
4) Hitting the ball - with straight arm or stretched VL=WR – the linear velocity of the ball
5) Landing - stable landing – shock absorplia by landing the knee.
Mechanical Analysis – data acquisition – data reduction – transfer raw data into useful form organized condensed.
Photographic Analysis System
A Cinematographic data reduction system includes the devices and routines involved in diglizing and mathematical analysis of film data.
Digitizing system used to put visual image into digital or numerical form, can be classified as these involve (i) Paper & pencil procedure (ii) Mechanical devices and procedure
(iii) Electronic devices and procedure
1) Paper & Pencil technique -
a) Body Contour technique
b) Point & line technique
2) A Mechanical digitizing devices - Mathematically analyzed.
3) Electronic digitizing devices – It can be interface directly.
Linear Kinematics
Distance and Displacement
When a body changes it position from one point to another. The distance represent the length of the path.
“It represent the magnitude of length- Distance”.
“Distance covered by the body during the motion” or
“Total path covered by the body during the motion”.
Displacement - If the distance covered in straight line between the starting and end line is called Displacement or
Minimum distance between two points.
Minimum distance or straight line jointing initial and final position.
Displacement refers the direction as well as magnitude.
Displacement may to zero or less than distance or equal
.
Speed - “The rate of change of position with time.
Distance covered in per unit time. Average Speed of the body is obtained by distance it covered by time. It take to cover that distance.
Speed is a scalar quantity.
Velocity - It is vector quantity. it has both magnitude as well as direction.
“Velocity is defined in as rate of change of motion of the body in a particular direction.
Average velocity – Distance conerved /unit time in a particular direction “Dividing displacement by time taken”
“ Velocity is also understood as rate of displacement or displacement per unit time”.
Acceleration - The term acceleration again represent a vector quantity.
“It is define as the rate of change of velocity”.
“The rate of which the velocity of a body changes with respect to time is known as its acceleration.
Average acceleration = Change in velocity
Time taken
= Final velocity – initial velocity
Time taken
ā = VF-VI
t
ā = Average acceleration
VF= The final velocity
Vi= The initial velocity
t = Time taken
If u is initial velocity & v is final velocity of an object & it take time t for velocity to change from u to v then acceleration is represent by ā = v-u = m/sec./sec.
t
If there is acceleration, there is change in velocity. There are two possibilities-
The acceleration may be + ive (increase) –ive(decrease) with regard to linear motion may called deceleration .
Acceleration due to gravity
All objects on or near the surface of the earth attracted toward it by gravity.
As object goes up the velocity reduces due to gravity is called retardation.

|

|
|
|
|
|

1. We require Trainees for marketing & promotion of our services, handsome stipend will be paid to selected candidates, Interested candidates can contact us.

1. Biomechanical analysis of takeoff technique in fos bury flop style in high jump.
2. Biomecanical analysis of fundamental skills of basketball.
3. Sports Bio-Mechanics working with cricket gurukul and carpotaral sports.